Depression facts
- Depression is a common mental disorder. Globally, more than 264 million people of all ages suffer from depression.
- Depression is a leading cause of disability worldwide and is a major contributor to the overall global burden of disease.
- More women are affected by depression than men.
- Depression can lead to suicide.
- There are effective psychological and pharmacological treatments for moderate and severe depression.
WHO January 2020
Depression prevalence and treatment success
- Point prevalence in Europe 6-8%
- Lifetime prevalence more than 20% Hinzpeter, Sass, Ziese (2019)
- Sales of antidepressants in Europe are more than 3.7 billions per year
- More than 6% of the population in Europe regularly take antidepressants. OECD (2015)
- About 60% of all depressed patients do not react properly to initial antidepressant treatments Dold, Kasper (2017)
- 30% of depression is related to treatment-resistant depressive disorders that do not react properly to the usual treatment with antidepressants (no or inadequate response to at least two different types of antidepressants in a sufficiently high dosage over a sufficiently long time span).
- „We found that all antidepressants which were included in the meta-analysis, were more efficacious than the placebo in adults with mayor depressive disorders and the summary effect sizes were predominantly modest“ Cipriani (2018) in The Lancet
- Treatment resistant depression was not taken into the account.
3 of 4 people suffering from major depression do not receive adequate treatment – WHO (2017)
Depression treatment with psychotherapy – facts
- Psychotherapy ist effective in the treatment of depression
- The availability is limited and usually only one hour per week or less
- In German S-3 guidelines psychotherapeutic treatment is always recommended for light to moderate depression
- “As far as the intensity and concentration of therapeutic influencesare concerned, psychotherapy may need to be reevaluated…The possibility exists, that many of today’s therapeutic efforts to change persistent problematic behaviors, are unsuccessful because of these influences. While, in theory they are correct, they are not intense or vigorous enough.“ Grawe (2004)
- The “weekly therapy hour”—in many cases, absent of any quality assessment ensuring reliance of evidence-based approaches—remains the practical default“. Schleider (2020)
Depression treatment with brain stimulation – facts:
- A strong, pulsating magnetic field stimulates certain parts of the brain
- Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is an evidence based treatment of mayor depressive disorder
- Level A evidence (definite efficacy) was reached for … HF-rTMS of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) using a figure-of-8 or a H1-coil for depression (Lefaucheur et al (2020)
- But: There are few treatment places and most psychiatrists do not know the procedure, even though it is recommended in the treatment guidelines
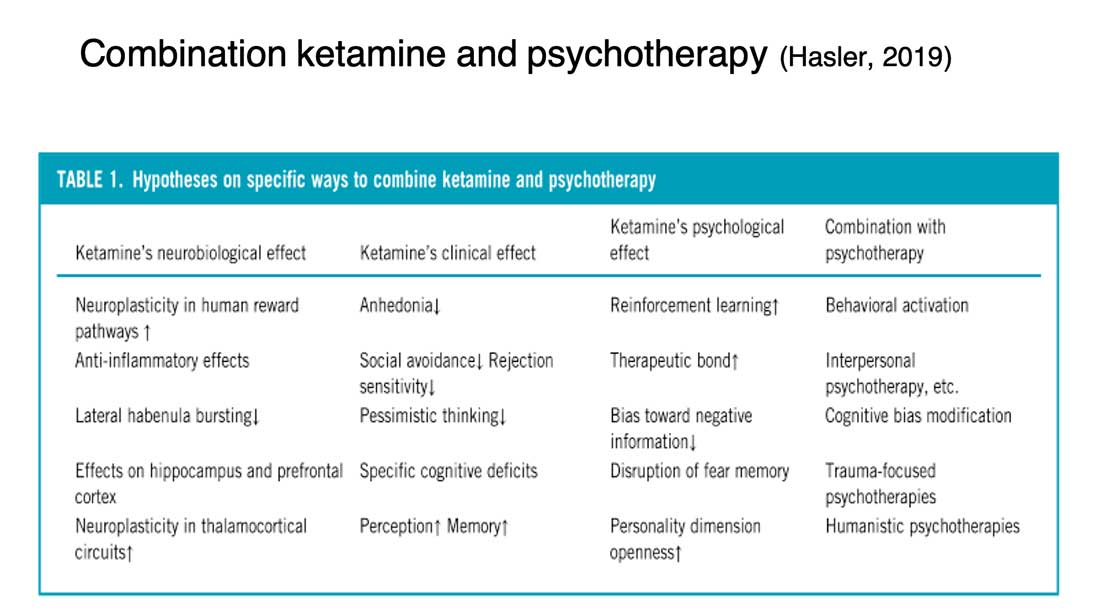
Combining Ketamine infusions with rTMS and high-frequent psychotherapy
- Ketamine leads to immediate improvement of symptoms and improves neuroplasticity
- rTMS also improves neuroplasticity and leads to longer lasting antidepressive effects
- Intensive psychotherapy (including hypnosis) benefits from the cognitive abilities improved by ketamine and rTMS and leads to long-lasting improvements
Ketamine facts
- Ketamine is on the market since 1970 as a dissociative anesthetic
- Ketamine is safe (ld 50 > factor 300 of therapeutic dose)
- Ketamine has few side-effects and no irreversible side-effects
- Ketamine has few contraindications: Uncontrolled hypertension, hyperthyroidism, intracranial pressure, severe heart failure, acute glaucoma, acute psychosis
- Ketamine has a short half-time
- No permanent intake of Ketamine is required: hit and go – effect
- The effects of Ketamine are extremly fast (within hours)
- Ketamine has fast anti-suicidal effects
“This is a game changer“ – John Krystal, MD, chief psychiatrist, Yale Medicine:
The drug works differently than those used previously, he notes, calling ketamine “the anti-medication” medication. “With most medications, like valium, the anti-anxiety effect you get only lasts when it is in your system. When the valium goes away, you can get rebound anxiety. When you take ketamine, it triggers reactions in your cortex that enable brain connections to regrow. It’s the reaction to ketamine, not the presence of ketamine in the body that constitutes its effects.”
How does ketamine work as depression treatment?
Mechanisms of action:
- Blocks the NMDA receptor and inhibits it allosterically
- Modulates and activates GABA A receptors of the α6β2δ and α6β3δ types.
- Weak agonistic effect at opioid receptors
- Inhibits reuptake of catecholamines at synaptic endplate
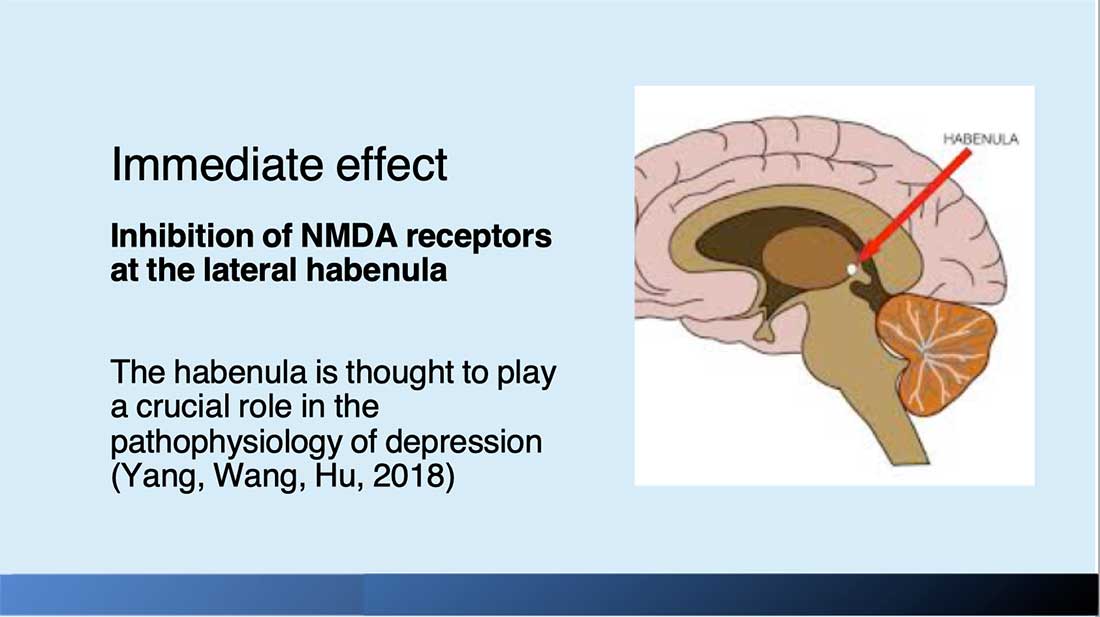
- Inhibition of NMDA receptors in lateral habenula with disinhibition of downstream reward centres (likely responsible for immediate effect)
- Micro RNAs expression of miR-29b-3p in the prefrontal cortex is increased, thereby positive effect on metabotropic glutamate receptor type 4
- Metabolite hydroxynorketamine probably has its own antidepressant potency
- Via glutamate AMPA receptor in the medial prefrontal cortex release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Increase in neuroplasticity
Chronic stress and depressive behaviours are associated in neuroscience research with impairments in neuroplasticity, such as neuronal atrophy and synaptic loss in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and hippocampus.
Ketamine increases connectivity and restores synaptic structures in the frontal brain and hippocampus
Ketamine administration is associated with the restoration of markers involved in molecular neuroplasticity, such as. Glutamate, AMPA (α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid) receptors, mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin), BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor), TrkB (tropomyosin receptor kinase B), VGF, eEF2K (eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase), p70S6K (p70 ribosomal S6 kinase), GSK-3 (glycogen synthase kinase 3), Erk, and microRNAs. M. Kang (2021)
Administration of Ketamine
- All the effects during the administration disappear usually within 20 to 30 minutes after infusion
- In few cases some effects can persist until the next day
- The patient must always maintain a sense of control. In case of undesirable side effects, the drip rate is reduced or the infusion is temporarily stopped
- The infusion must be administered in a quiet, safe environment
- The patient must be able to communicate with the therapist at all times. Blood pressure and oxygen are continuously monitored
Immediate effects of ketamine infusions
- Improvement of depressive symptoms on the next day, sometimes already during or shortly after the infusion.
- Reduction or disappearance of suicidal thoughtsReduction in anxiety, compulsions and pain
These effects last for days to weeks, in rare cases even permanently.
Some patients experience significant effects after the first infusion, some patients require a series of up to six infusions, very rarely more.
We usually administer an infusion every second day, in severe cases initially daily. Longer intervals are also possible.
Possible side effects of ketamine infusions
- Feeling of being drunk
- Change in colour and shape perception, double vision
- Change in body perception
- Memorizing forgotten experiences
- Eurphoria, silliness
- Dreams, mild hallucinations
- Feeling of merging with the environment
- Increased sensitivity to sound
- Nausea
- Panic attacks due to the experience of dissociation
- Increase in blood pressure
IV Ketamine Treatment or Esketamine nasal spray?
The patent on racemic ketamine has long expired. So intravenous ketamine for treatment of depression cannot be patented, and the pharmaceutical industry has therefore no incentive to undertake costly clinical trials to obtain a marketing permit. This is why it remains an off-label treatment
Esketamine nasal-spray was patented by Janssen and is approved for treatment resistant depression.
Esketamine nasal spray is less safe, less controllable and less effective than racemic ketamine – Bahji, Vazquez, Zarate (2021)
The price of esketamine nasal spray is about 500 euros per dose. It may only be given under inpatient conditions by healthcare professionals.
So the nasal spray is a good business!
What is Transcranial magnetic stimulation?
When a strong alternating magnetic field is directed on parts of the brain, the neurons are forced to depolarize. The magnetic field makes them release the neurotransmitters that regulate brain functions.
Unlike depression medications, TMS does not have systemic effects such as weight gain, sexual dysfunction, nausea, tremors, dry mouth, diarrhea, headaches, constipation, sweating, sleepiness or anxiety. It also does not generate any cognitive impairment that was observed in ECT treatment such as memory impairment and no anesthesia or muscle relaxant medication are needed.
- 1995 first studies about depression treatment with rTMS (George et al)
- 2008 FDA approved for patients with MDD who failed one medication
RTMS for depression treatment
- A series of 20 stimulations 10 Hz over the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex reduces robustly depressive symptoms
- In patients with unipolar depression effects are the same or better than with pharmacotherapy. -Lefaucheur (2020)
- Modern, more intensive treatment programs (Stanford Accelerated Intelligent Neuromodulation Therapy SAINT) show remission rates of almost 90% with 10 stimulations daily for 5 days -Cole et al (2020)
- Effects sustain over months – Donse et al (2017)
How to target the correct stimulation area with rTMS:
Orientation to the scalp via anatomical calculation models are unreliable because there are large interindividual deviations in the exact position of the DLPFC.
MRI-guided neuronavigation is costly and does not necessarily provide a reliable additional benefit in terms of efficiency.
We use a neuro-cardiac-guided TMS that measures the effect of probatory stimulation on heart rate deceleration. – Iseger et al (2020)
Possible side effects of rTMS:
Rare and harmless:
- Headache
- Drowsiness
Extremely rare:
- Seizures (usually in patients with pre-existing epilepsy)
EEG Neurofeedback Training for depression treatment
In EEG neurofeedback, EEG patterns are linked in real time with animations on a screen. Through operant conditioning, brain activities in certain areas can be strengthened or weakened. The procedure is non-invasive and safe.
Neurofeedback training is well established and proven effective for ADD/ADHD
There is certain evidence of the effectiveness of neurofeedback training in the treatment of depression (Barlas, 2021).
Studies on the combination with ketamine are not yet known.
Psychotherapy for depression treatment
There are hundreds of different psychotherapy methods.
Even in the application of the individual procedures, there are great differences in the training of the therapists and the implementation of the treatment. The intensity and frequency of application differs considerably. Treatments are carried out individually or in groups
There are therefore considerable methodological problems in comparing the effect of the procedures with regard to their effectiveness in depression.
- Cognitive Behaviour Therapie (CBT) shows generally positive effects in the treatment of depression (Lopez et al, 2019)
- Psychodynamic Therapy seems to have comparable effects to CMB (Steinert et al, 2017)
- EMDR (eye-movement-desensitisation-and-reprocessing), a procedure developed for the treatment of trauma patients, also seems to be effective (Wood et al, 2018)
- Hypnosis also seems to be effective (Milling et al, 2019)
- Gestalt-Therapy seems to be effective, but not as effective as hypnosis (Gonzalez-Ramirez, 2017)
Combination rTMS and Ketamine for depression treatment
Combination therapy with transcranial magnetic stimulation and ketamine for treatment-resistant depression: A long-term retrospective review of clinical use (Best et al. 2019)
Ketamine therapy combined with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for major depressive disorder at a suburban tertiary clinic (Davila et al, 2021)
Various studies, not only for the treatment of depression, show clear evidence of a synergistic effect of rTMS and ketamine, as well as good tolerability and safety.
Combination Psychotherapy and Ketamine for depression treatment
Krupitsky E.M. & Grinenko, A.Y (1997) Ketamine psychedelic therapy The positive role of spiritual experiences for the treatment of alcohol dependence is reported here
Samuel Wilkinson (2018): Cognitive Behavior Therapy May Sustain Antidepressant Effects of Intravenous Ketamine in Treatment-Resistant Depression. Cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) after i.v. ketamin-infusions
Raquel Bennett (2019): i.m. or sublingual Ketamine 0,5mg/kg leads to consolidation of psychological material in a psychotherapy. 1,0-2,0 mg/kg i.m. induces a psychedelic Ketamine journey. In both cases, ketamine is ultimately used as a kind of catalyst for psychotherapeutic processes
Dore, J et al (2019) Ketamine assisted psychotherapy (KAP): Patient demographics, clinical data and outcomes in three large practices administering ketamine with psychotherapy This article is the first to explore KAP within an analytical framework examining three distinct practices that use similar methods. Especially in elderly patients and patients with severe symptoms, lasting improvements are achieved.
Treatment concept for depression Dr. Scheib
In the practices Dr Scheib in Munich and Berlin and the clinic Dr. Scheib on Mallorca, we combine ketamine infusion therapy with intensive psychotherapy, hypnosis, magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and neurofeedback.
In addition, we offer – depending on the indication and location – sports therapy, physiotherapy, biofeedback and other relaxation methods.
At the beginning, an intensive psychiatric and psychological assessment takes place, including EEG and psychological test diagnostics. This is followed by a common therapy plan in which the individual elements are combined depending on the patient’s problems and resources.
On average, each patient receives between four and six ketamine infusions at intervals of one to two days. In addition, there are around 10 (sometimes more) hours of psychotherapy per week. 10, in special cases up to 50 units of rTMS per week, and additionally daily neurofeedback other relaxation procedures (depending on whether it is inpatient or outpatient treatment)
Follow-up survey 116 patients between April 2017 and February 2021:
26 patients responded
Age between 19 and 82 years
Average of two and a half years after treatment (3 to 49 months)
Average of 5 ketamine infusions (0.5mg/kg)
Ketamine only 19%, ketamine plus other procedures 81%
Additional psychotherapy 65%
Additional rTMS 35%
Additional neurofeedback 23%
If you are the caregiver for a person with dementia and feel overwhelmed, we can help. We will be happy to answer your questions personally:
For further information please feel free to contact us:
Write us, we will get back to you as quickly as possible: